
Due to the prolongation of human service life, the increase in the number of enterprises injured by diseases and the application of some research drugs, including dysphagia (DD) caused by abnormal pharyngeal and esophageal functions and structural characteristic lesions, the incidence of dysphagia (DD) is increasing significantly.
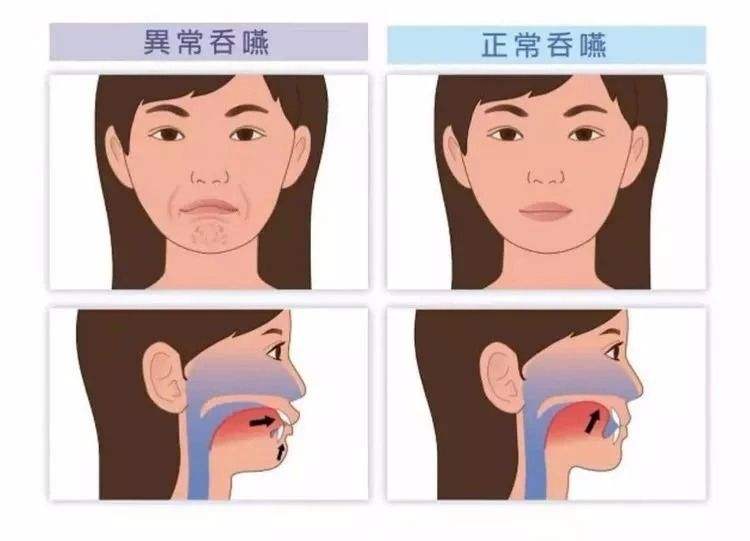
At the same time, with the improvement of people's quality of life, dysphagia caused by various conditions and its possible severe poor prognosis have also begun to attract the attention of clinicians.
Knowing that swallowing is a reflex behavior requires good coordination of the functions of the mouth, throat and esophagus, and the coordination of the swallowing process is controlled by the swallowing center of the brain stem.
The common dysphagia in clinic is true bulbar palsy caused by injury of glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, hypoglossal nerve nucleus and subnuclear nucleus, and/or pseudobulbar palsy caused by injury of bilateral cortical brainstem bundle, that is, bulbar palsy and pseudobulbar palsy are more common in patients after stroke. The dysphagia is mainly caused by delayed random tongue movement and decreased coordination of muscle movement related to swallowing.
Temporary dysphagia may also occur in patients with unilateral cortical brainstem injury.
Dysphagia is a common complication after stroke. It is reported that dysphagia can be detected in 30-65% of acute stroke patients, and it is also reported that 57-73% of stroke patients have dysphagia, and a few of them are clinically manifested as "asymptomatic" inhalation of food or liquid, that is, silent inhalation.
Physiological oral stage of swallowing
The coordinated development of the movement and sensation of one's own teeth, tongue, lips and cheek muscles can form a chewing movement, so that the material culture entering the Chinese oral cavity can form a food ball or liquid and push it to the pharynx.
1. Pharyngeal stage
The velum palatini lifts the muscles, the velum palatini tension muscles contract to lift the soft palate, the suprahyoid muscles contract in front of the hyoid bone, the pharyngeal structure rotates forward along the longitudinal axis, the vocal cord is closed, the arytenoid muscle and the closed throat entrance fatigue, and the arytenoid cartilage moves inward to close the throat vestibule.
The contraction of the tongue and pharynx combined with the gravity mission enters the esophagus through the circumpharynx. The contraction of the pharyngeal muscle shortens the long axis, the vestibule of the larynx and the pear shaped recess disappear, and the pharyngeal sphincter contracts in turn, pushing down the mass or liquid, and removing food residues.
2. Esophageal stage
The upper esophageal sphincter relaxes by inhibiting the contraction of the pharynx and around the pharynx, enabling food to pass through the esophagus.
The basic structural features of normal swallowing can be summarized and analyzed as follows: to achieve and maintain control over the food mass; By generating different pressures, the food group can be promoted to pass through the pharynx as soon as possible; Shorten the time when the patient's respiratory system stops working to the greatest extent; Prevent food or liquid from squeezing into the nasopharynx or throat; Prevent reflux of gastric contents during esophageal emptying; Eliminate food residues in pharynx and esophagus.
Abnormality in the pathological oral stage of swallowing
Loss of tongue sense, tongue muscle paralysis, lip or facial muscle dysfunction can cause saliva accumulation, salivation, and dyslexia; 2/3 of the front tongue movement abnormalities can lead to food lifting, shaping and propulsion obstacles, and tongue back and forth movement is invalid; A variety of reasons lead to decreased saliva secretion in the mouth, and dry mouth can cause swallowing.
Pharyngeal phase abnormality: the soft palate can not be lifted or the superior pharyngeal sphincter is weak in contraction, paralysis causes pharyngeal food retention, and the strength of the back of the tongue is weakened;
Dysphagia can be caused by abnormal sensation of the throat or pharyngeal movement disorder, such as poor laryngeal closure, poor UES relaxation, and uncoordinated UES relaxation and pharyngeal advancement during swallowing, and denervation of the feeding tube.
In a word, swallowing disorder can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as striated muscle paralysis and incomplete paralysis, oropharyngeal sensory retardation, swallowing reflex retardation or loss caused by injury of cortex and brainstem swallowing center, and swallowing motor coordination disorder, such as loss of high inhibition of medullary center and persistent hyperreflexia.
In addition, coordination of breathing and swallowing is necessary to prevent food from seeping into the airways.
Treatment strategy
Logemann divides the summary of treatment strategies into three categories: direct strategies, indirect strategies and compensation strategies. Before doing these three treatment strategies, the first or most important thing is to improve oral care and general condition at the same time.
Direct strategy
1. Feeding position If the patient is in supine position, his trunk should be raised by 30 degrees, his head and neck should be bent forward, and the shoulder of the hemiplegic side should be cushioned with a pillow, so as to reduce the risk factors of countercurrent through the nasal cavity and also reduce the miscarriage of pharynx; If it is in a sitting position or the trunk is kept at a natural forward inclination of about 20 degrees, the neck will flex slightly forward, so that the tension of hyoid muscle will be significantly increased, and the throat will be lifted up, so that food can easily enter the artificial esophagus, and swallowing movement reflex can be easily induced by swallowing;
When eating, the body leans 45 degrees to the healthy side, so that the healthy side pharynx expands to facilitate the development of food.
In addition, the neck rotates 90 degrees to the hemiplegic side, which not only increases the pharynx of the healthy side, but also reduces the residual food in the pear shaped recess.
2. Before cold stimulation treatment for swallowing, touch the pharynx arch with cold laryngoscope or immerse the frozen cotton swab in small water. Gently, touch and stimulate the posterior palatal arch, soft palatal arch, palatal arch, posterior pharyngeal wall and posterior tongue for 20 times in the afternoon to make the trigger swallowing reflex area sensitive, effectively strengthen the swallowing reflex, and then swallow briefly.
Cold stimulation treatment before oral feeding can improve the sensitivity of food blockage perception, and improve the attention to eating and swallowing through stimulation, thus reducing false pharynx. If necessary, stop vomiting reflex to avoid suffocation and swallowing errors.
3. Take a rest 30 minutes before the meal and prepare for the meal. The environment should be quiet. The sunshine and lighting should be bright and comfortable.
Choose foods acceptable to the patient, such as food that is easy to swallow, appetizing food, and warm food that can stimulate the swallowing reflex.
It can be frozen or pasty, viscous and not loose, and it will not remain on the mucous membrane when passing through the pharynx and esophagus.
It can be confirmed first and the patient's ability to swallow problems can be started from rice paste, egg soup, porridge and other pasty foods, and gradually develop to add solid substances such as rotten rice, cooked radish, and choose smooth food with uniform density, not too sticky, and not too loose; Fruit juice is better than water when you feed it.
Start feeding with small spoons, and the amount of food increases gradually from decreasing. When eating, pay attention to the proper size of the food group, enter the oral cavity side, and then gently press the tongue with a spoon to stimulate the swallowing reflex. You should swallow several times, so that all the food that passes through the throat is given water to rinse the mouth after the food, to avoid food residues caused by accidental swallowing.
Indirect Strategy - Indirect Swallowing Training
First of all, ice massage neck, cheek and pharynx, training and relaxation of neck joint range of motion, active and passive movement and pronunciation training around the mouth;
Training, respiratory system training, cough training, etc. In addition, there are other indirect management methods learned from other enterprises, such as supraglottic swallowing, also known as autonomous airway protection, which requires that patients can hold their breath before and during swallowing, and then close the true vocal cords;
1. Mendelsohn method
It is a method to independently extend and strengthen the throat lifting and prepositional movement to enhance the opening of the cricopharyngeal muscle in different degrees during swallowing. The specific practical operation technology can support the throat with hands while the throat is rising; Percutaneous electrical stimulation is to place electrode materials on the neck for one hour per day;
2. Breath holding vocal movement
Push the wall with both hands at the same time, or sit, hold your breath and inhale. When the chest is fixed, the glottis is closed, then suddenly exhale, and the glottis is wide open. (This action can train the inspiratory function of the glottis, strengthen the muscle strength of the soft palate, and help clear the remaining food in the pharynx);
3. Operation to promote swallowing reflex
The purpose is to stimulate and restore the sensation of swallowing muscles and induce swallowing reflex.
The method is to rub the skin down the jaw along the thyroid cartilage
4. Laryngeal adduction training is to form a closed vocal cord for training and hum to induce glottic atresia;
5. Pronunciation training (basic training of swallowing function) Say "a", move "yi" to both sides, and then move to "wu".
Make the "f" sound or whistle again, three times each time, 5-10 times consecutively, 2-3 times a day, and promote the lip muscle movement through opening and closing the mouth;
6. Facial and mandibular movements
Use suction to contract the cheek, part and orbicularis oculi muscle, then open and close the mouth, bulge the cheek, and chew the chin three times a day
7. Tongue muscle training
(1) Let the patient stretch out his tongue, then move left and right towards the baby pigeon, lick the lower lip with the tip of his tongue, then turn to lick the upper lip, and finally press the hard palate upward with his tongue, repeating three times a day.
(2) If the patient's tongue can not pass the movement, the tongue depressor or spoon can be used to study and massage the tongue, or the gauze can be used to wrap the tongue gently to carry out these movements outside the people who can move up and down the enterprise.
Compensatory strategy
It is the posture and method used when swallowing, and it makes swallowing safe by changing the food channel and specific swallowing method.
1. Turn your head, that is, swallow laterally
Turn the head to the pharyngeal paralyzed side, make the food bypass the front of the throat, remove the "pear shaped fossa" on both sides of the pharynx, and enter the esophagus from the normal side of the pharyngeal muscle through the upper esophageal sphincter;
2. Lower jaw position
It can expand the space of epiglottis, make epiglottis move backward, and protect airway.
If you swallow alternately, you can swallow different forms of food, such as solid food and liquid food, which is helpful to remove pharyngeal residues;
3. Nodding swallowing
The epiglottis valley is another part that is easy to analyze food residues. When the neck is chin up, the epiglottis valley will become narrower, and the food resources for residual food can be squeezed out. Then the neck can be chin down as far as possible, which looks like a nod, while doing empty swallowing function, so that food can be detected by removing these residues;
4. Random cough
Let food enter the airway and it will cough out.
Gastrointestinal nutrition awareness disorder
The protective cough caused by repeated respiratory infection, severe mental retardation, moderate to severe dysarthria, severe dysphagia with a large amount of aspiration or "quiet" aspiration (asymptomatic aspiration) disappears. You must first fast, use intravenous nutrition, and then use nasal feeding after fluid supplement.
If the patient's dysfunction cannot be recovered 2 weeks after the insertion of the nasogastric tube (also 4 weeks later), it should be changed to gastrostomy (PEG) as far as possible.
Because of the mechanical interference of the nasogastric tube, the partial blockage of the nasal airflow, and the dry oral mucosa caused by forced oral breathing, the spray gate sphincter is always open during nasal feeding, which will aggravate the difficulty of swallowing.
Gastroesophageal reflux is easy to occur, which can cause dysphagia and aggravate pneumonia. Stimulating the nasogastric tube can make the pharynx and esophageal mucosa secrete excessive fluid, causing silent aspiration.
In addition, the nasogastric tube can still stimulate the patient's appetite, so the feeding time of the nasogastric tube should be shortened as far as possible in clinical practice, and the bedside should be raised by 30-40 degrees for 2 hours after the nasogastric tube feeding, and excessive feeding should be avoided.
PEG is a kind of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), which is easy to operate and can also be tolerated by critically ill patients. As a stroke patient, PEG has difficulty swallowing, that is, under the guidance of endoscopy, the neogastrostomy can extend to the distal pylorus to the direct intestine, which can reduce the complications of nasosinusitis and nasogastric feeding tube placement through intestinal feeding and preserving gastrointestinal decompression function. Especially, with the incidence of aspiration pneumonia, PEG complications are less, However, there is a dispute about when to start. It is generally believed that oral feeding can not recover in a short time, and PEG should be changed to two weeks after gastric tube operation.
Acupuncture and electroacupuncture for treatment of electric stimulation
Acupuncture and electroacupuncture can stimulate the muscles of the pharynx and larynx, prevent the disuse atrophy, and increase the activity of the brain nerves in the economically damaged areas by continuously stimulating them. Repeated stimulation of the senior management motor center that excites the brain can help China recover and reconstruct the normal reflex arc, and promote the formation of a new central to pharynx motor information transmission pathway.
The central nervous system has a high degree of plasticity. Continuous stimulation leads to the strengthening or reconstruction of central synapses and the reorganization of the nervous system. Repetitive electrical stimulation can compensate for dormant synapses.
Modern research shows that acupuncture can produce many "endogenous drug factors" such as infrared radiation, particle flow and electromagnetic in the body, increase catalase in human mitochondria, and thus promote cell metabolism.
Electroacupuncture can improve the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), enable the body to effectively remove free radicals, improve its ability to avoid excessive reactive oxygen attack, reduce brain tissue damage, improve the compensatory capacity of brain tissue, increase brain metabolism and nutrition, promote the recovery of neurotransmitter transmission function, and repair damaged brain tissue.
other
1. Drug and surgical treatment
It includes drugs that can inhibit the saliva secretion of patients, such as artan, and shorten the delayed working time that triggers the swallowing and passage of food pellets, such as nifedipine.
Tracheotomy is beneficial to ventilation and airway clearance, but the intubation time should not be too long, because the intubation affects the lifting of the larynx and the relaxation of the cricopharyngeal muscle.
There are also circumpharyngotomy, epiglottis remodeling, partial or total removal of cricoid cartilage, laryngeal suspension, and laryngotracheal separation. Long term severe dysphagia should be treated with laryngectomy, or even laryngectomy to reconstruct the respiratory tract.
2. Psychotherapy
Apoplexy patients have difficulty swallowing. Due to their different degrees of limb paralysis or aphasia, unclear language, unclear expression, etc., they are prone to fear, inferiority, tension and other emotions. Therefore, medical staff and family members should give comfort and care about diet. Patients should be guided and encouraged. Patients should have confidence to overcome the disease, strive to eliminate bad psychology, actively cooperate with doctors, eat on time, and strengthen their physique, Promote health.
3. Drug induced dysphagia
For some drugs, such as sedatives (delayed swallowing reflex), hypnotics (central inhibition), anticholinergics (antagonistic to ACH release), dopaminergic drugs and drugs that block nerve muscle connection: Botulinum toxin type A, etc., It can reduce or stop dysphagia and alleviate dysphagia in a certain time.
4. Precautions
In case of cough and obvious cough, the patient should bend down, lean forward, lower the jaw to the chest, and prevent the residue from invading the airway again. If the food residue is stuck in the throat and endangers breathing, the patient should bend down again, and the rehabilitation technician can rapidly develop and continuously flap the residue out of the patient's treatment shoulder; You can also stand at different patients and their backs, with your arms under the chest, your fingers crossed, and exert a positive upward jerking force on the diaphragm. The resulting airflow does not pass through the epiglottis, and can discharge the obstruction.
Prevent suction, prohibit straw from drinking water, and avoid entering the trachea by mistake. Use a cup to drink plain water. If the water is less than half a cup, the patient will go back to drink water. This posture will increase the risk of aspiration.
Another way to prevent accidental inhalation is to let the patient inhale enough air before eating, hold the breath before and during swallowing, close the vocal cords, cough after swallowing, and expel air from the lungs.
So as to discharge the food residues left in the throat.
To sum up, we have refined almost all rehabilitation strategies for dysphagia at home and abroad.
In specific clinical practice, some specific rehabilitation methods were selected for patients:
No matter what kind of disease causes functional abnormality, it can be divided into three levels of disability, disability, disability, and rehabilitation methods of treatment, compensation and adaptation.
For dysphagiaThe purpose of treatment is to promote the recovery of social function. For example, the muscle strength and coordination of the swallowing muscle can be improved through the training of the swallowing muscle. The purpose of compensation is to adopt a certain head position or swallowing strategy to reduce the occurrence of aspiration and promote food intake.
Generally, various rehabilitation education methods at different levels can be adopted at the same time.
Shandong Zhushi Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd., founded in 2003, has more than 5000 registered employees. After years of development, it has developed into a diversified industrial cluster integrating medical devices, polymers, cosmetics, health food, daily necessities and biological reagent production, enterprise management consulting and training, real estate economy, pharmaceutical transportation, pharmaceutical printing, etc.
Adhering to the concept of life, health and happiness, the Group provides you with full chain health services.
HOT
NEW